2026

WHU-PCPR: A multi-platform heterogeneous point cloud dataset for place recognition in complex urban scenes
Xianghong Zou, Jianping Li†, Yandi Yang, Weitong Wu, Yuan Wang, Qiegen Liu†, Zhen Dong
ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing (IF: 12.2) 2026
Point Cloud-based Place Recognition (PCPR) demonstrates considerable potential in applications such as autonomous driving, robot localization and navigation, and map update. In practical applications, point clouds used for place recognition are often acquired from different platforms and LiDARs across varying scene. However, existing PCPR datasets lack diversity in scenes, platforms, and sensors, which limits the effective development of related research. To address this gap, we establish WHU-PCPR, a cross-platform heterogeneous point cloud dataset designed for place recognition. The dataset differentiates itself from existing datasets through its distinctive characteristics: 1) cross-platform heterogeneous point clouds: collected from survey-grade vehicle-mounted Mobile Laser Scanning (MLS) systems and low-cost Portable helmet-mounted Laser Scanning (PLS) systems, each equipped with distinct mechanical and solid-state LiDAR sensors. 2) Complex localization scenes: encompassing real-time and long-term changes in both urban and campus road scenes. 3) Large-scale spatial coverage: featuring 82.3 km of trajectory over a 60-month period and an unrepeated route of approximately 30 km. Based on WHU-PCPR, we conduct extensive evaluation and in-depth analysis of several representative PCPR methods, and provide a concise discussion of key challenges and future research directions.

2025
LifelongPR: Lifelong knowledge fusion for point cloud place recognition based on replay and prompt learning
Xianghong Zou, Jianping Li†, Zhe Chen, Zhen Cao, Zhen Dong, Qiegen Liu†, Bisheng Yang
IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems (IF: 8.4) 2026
Point cloud place recognition (PCPR) is a fundamental task in robotics and computer vision in the fields of autonomous driving, intelligent transportation, and augmented reality. To cope with the dynamic changes in scenarios and sensor types, PCPR models need to incrementally acquire, update, and accumulate knowledge for continuous evolution—an ability known as continual learning (CL). However, due to the dynamic distributions of incrementally acquired point cloud data, PCPR models often forget previous knowledge when acquiring new knowledge, i.e. catastrophic forgetting. To address this issue, this study proposes a novel CL method tailored for PCPR, which effectively extracts and fuses knowledge learned by the model across sequential point cloud data. First, a replay sample selection method is proposed, dynamically allocating a replay sample size to each training set based on information quantity and selecting replay samples based on spatial distribution. Second, a new CL framework composed of a prompt module and the two-stage training strategy is proposed, and the domain-specific knowledge captured from each training set by the prompt module is used for guiding the backbone network to extract features adapted to individual samples. Comprehensive experiments on large-scale public and self-collected datasets are conducted to validate the effectiveness of the proposed method. Compared with state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods, our method achieves 6.50% improvement in 𝑚𝐼𝑅@1, 7.96% improvement in 𝑚𝑅@1, and an 8.95% reduction in 𝐹.

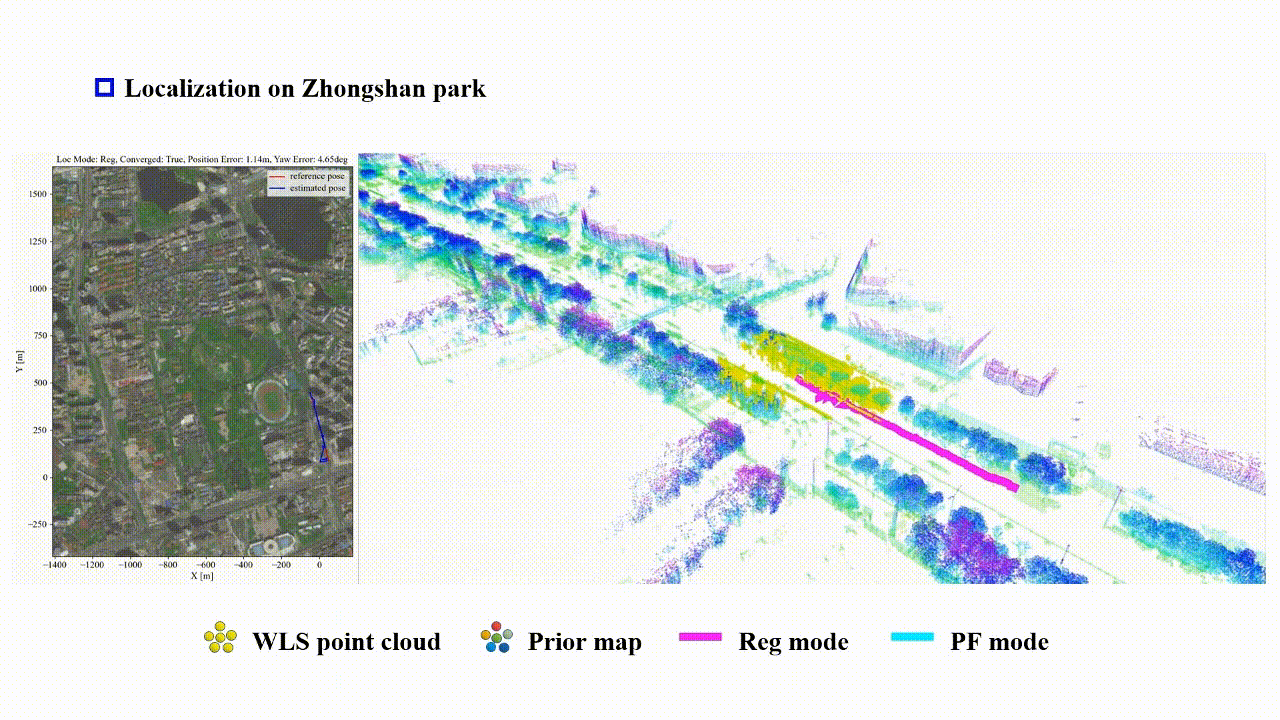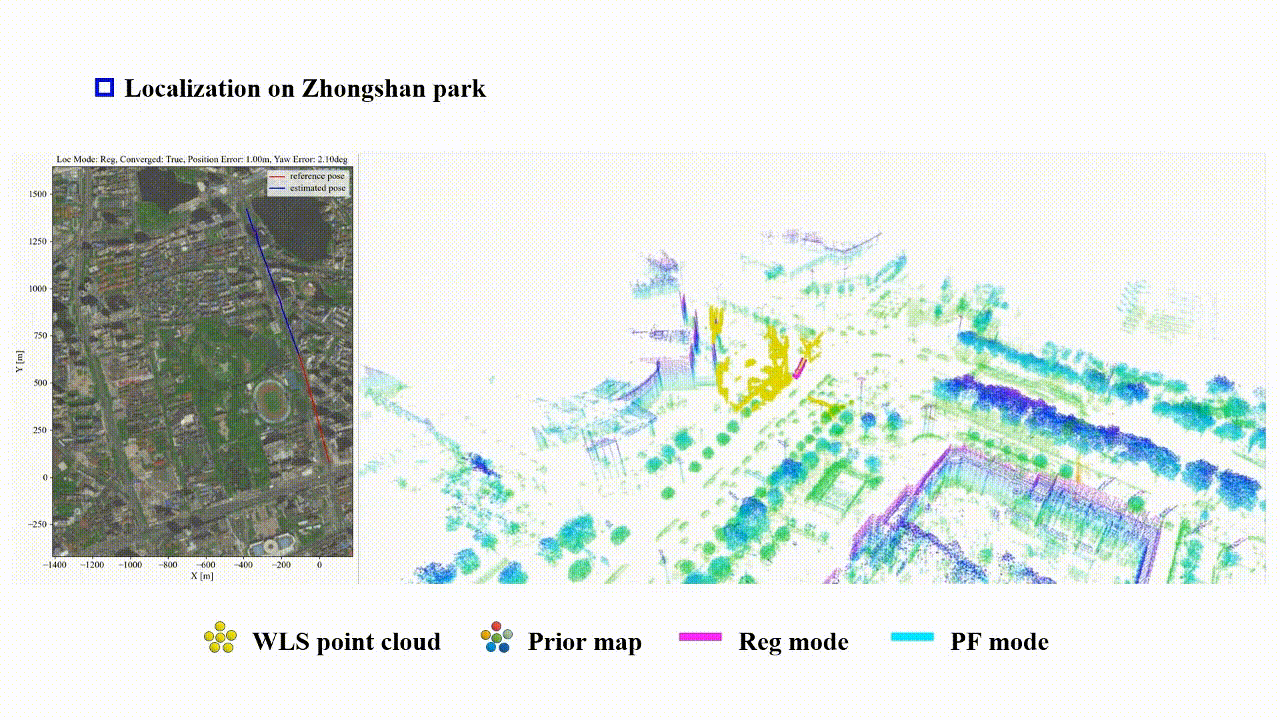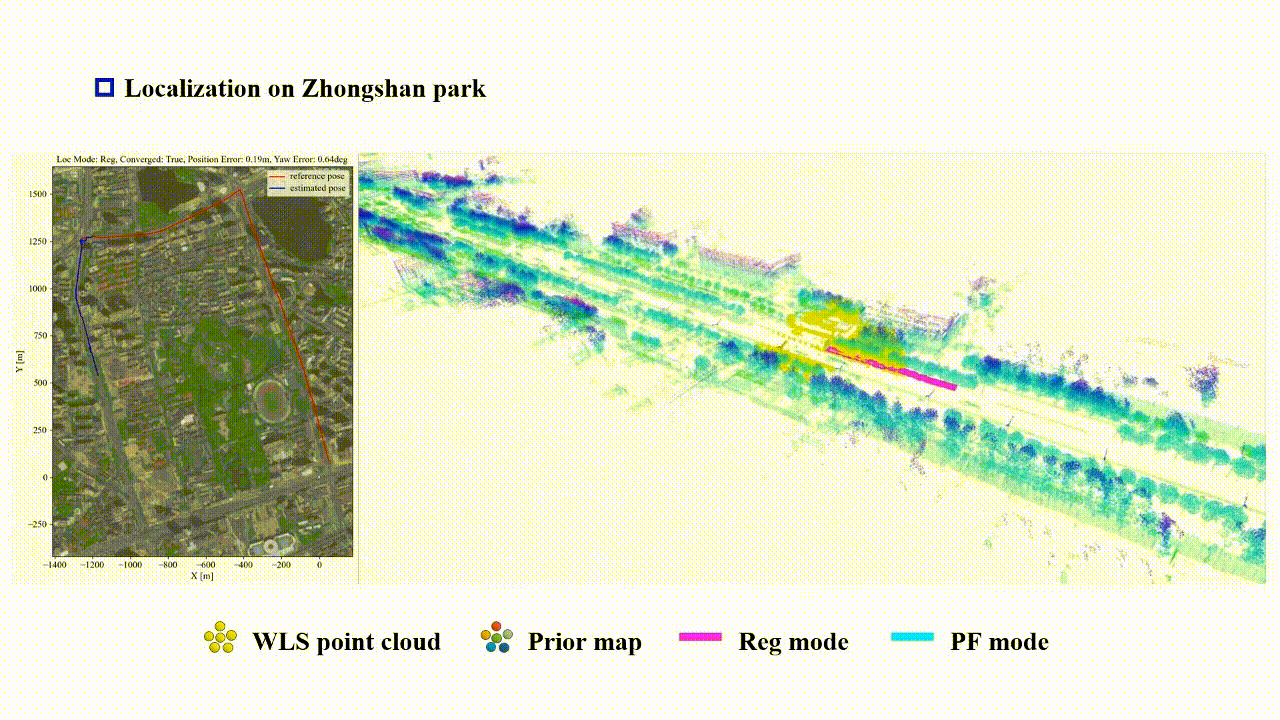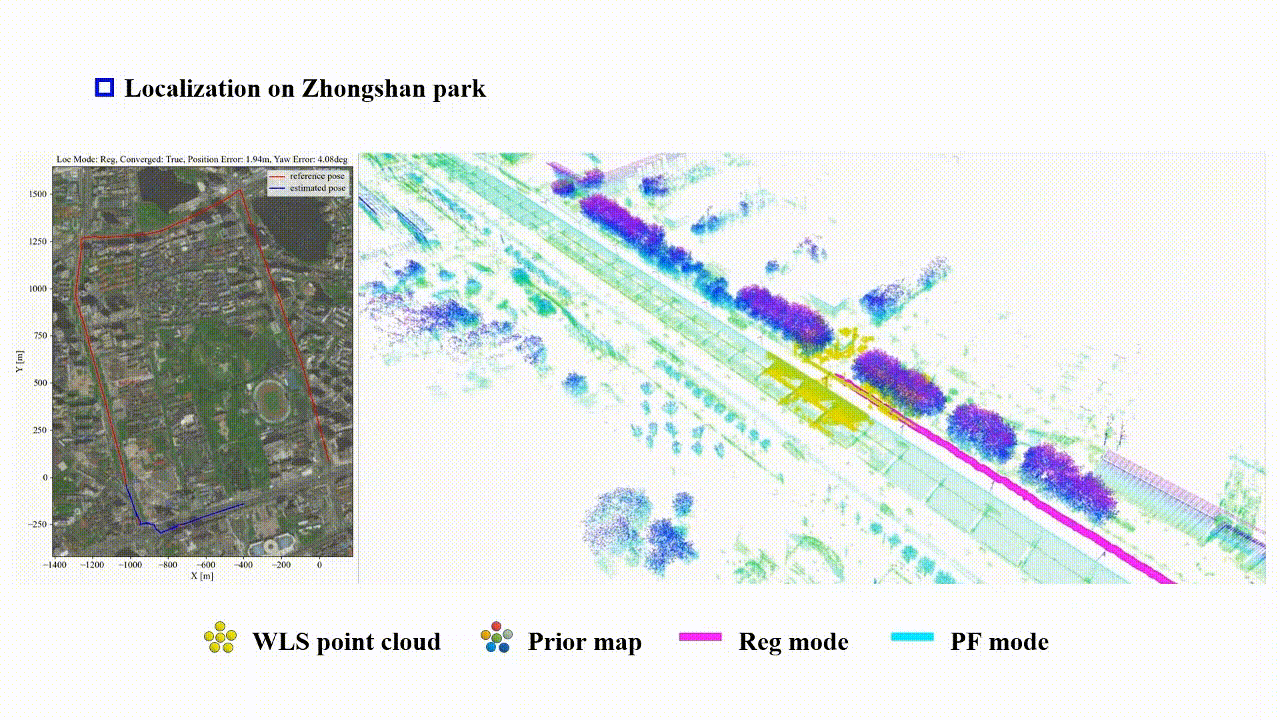
Reliable-loc: Robust sequential LiDAR global localization in large-scale street scenes based on verifiable cues
Xianghong Zou, Jianping Li†, Weitong Wu, Fuxun Liang, Bisheng Yang†, Zhen Dong
ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing (IF: 10.6) 2025
We propose a LiDAR-based reliable global localization method, Reliable-loc, which achieves better robustness in complex large-scale outdoor scenes with insufficient features and incomplete coverage of the prior map. The experimental results indicate that Reliable-loc exhibits high robustness, accuracy, and efficiency in large-scale, complex street scenes, with a position accuracy of ±2.91 m, yaw accuracy of ±3.74 degrees, and achieves real-time performance.

2023
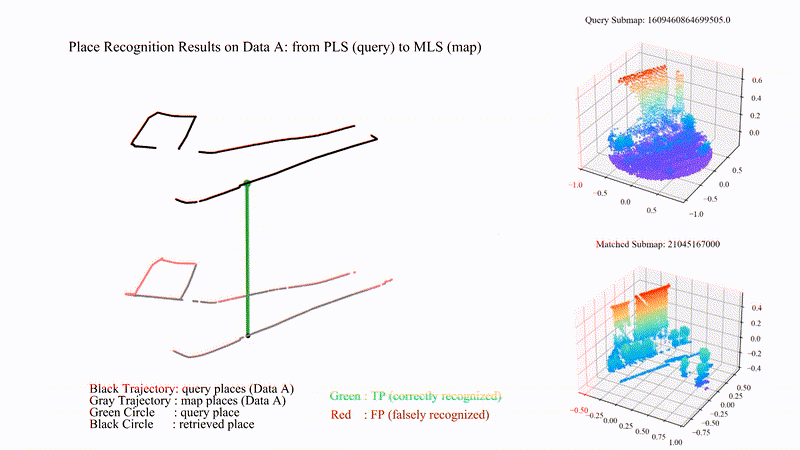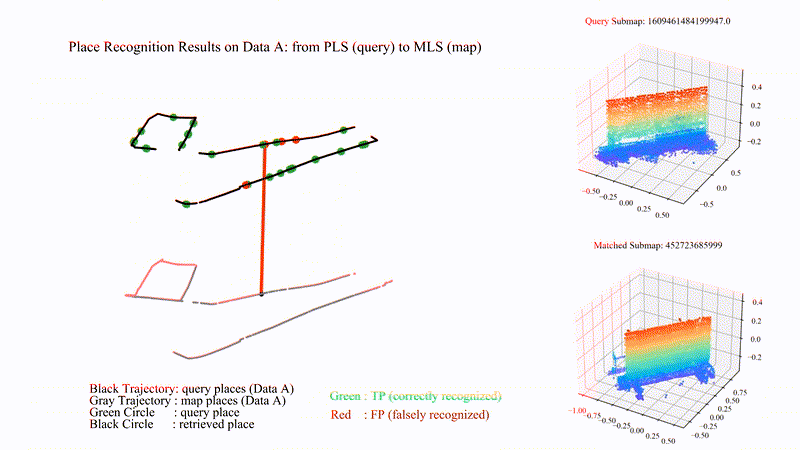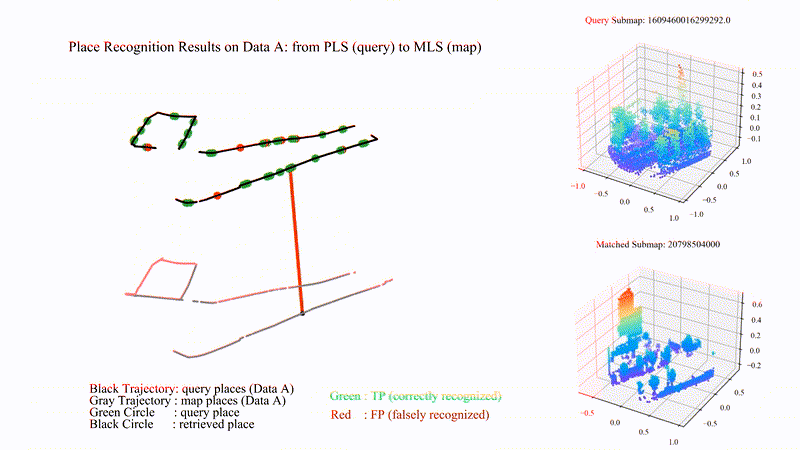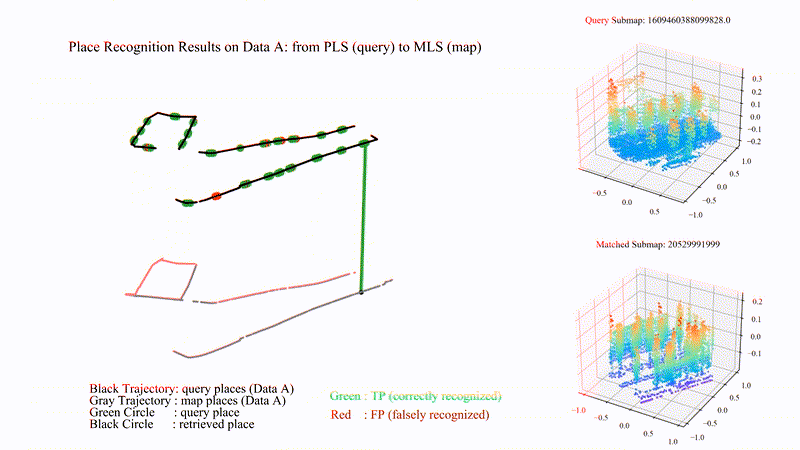
PatchAugNet: Patch feature augmentation-based heterogeneous point cloud place recognition in large-scale street scenes
Xianghong Zou, Jianping Li†, Yuan Wang, Fuxun Liang, Weitong Wu, Haiping Wang, Bisheng Yang†, Zhen Dong
ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing (IF: 12.7) 2023
We propose PatchAugNet, which utilizes patch feature augmentation and adaptive pyramid feature aggregation to achieve better performance and generalizability for Heterogeneous Point Cloud-based Place Recognition (PCPR) tasks. The comprehensive experimental results indicate that PatchAugNet achieves SOTA performance with 83.43% recall@top1% and 60.34% recall@top1 on unseen large-scale street scenes, outperforming existing SOTA PCPR methods by +9.57 recall@top1% and +15.50 recall@top1, while exhibiting better generalizability.

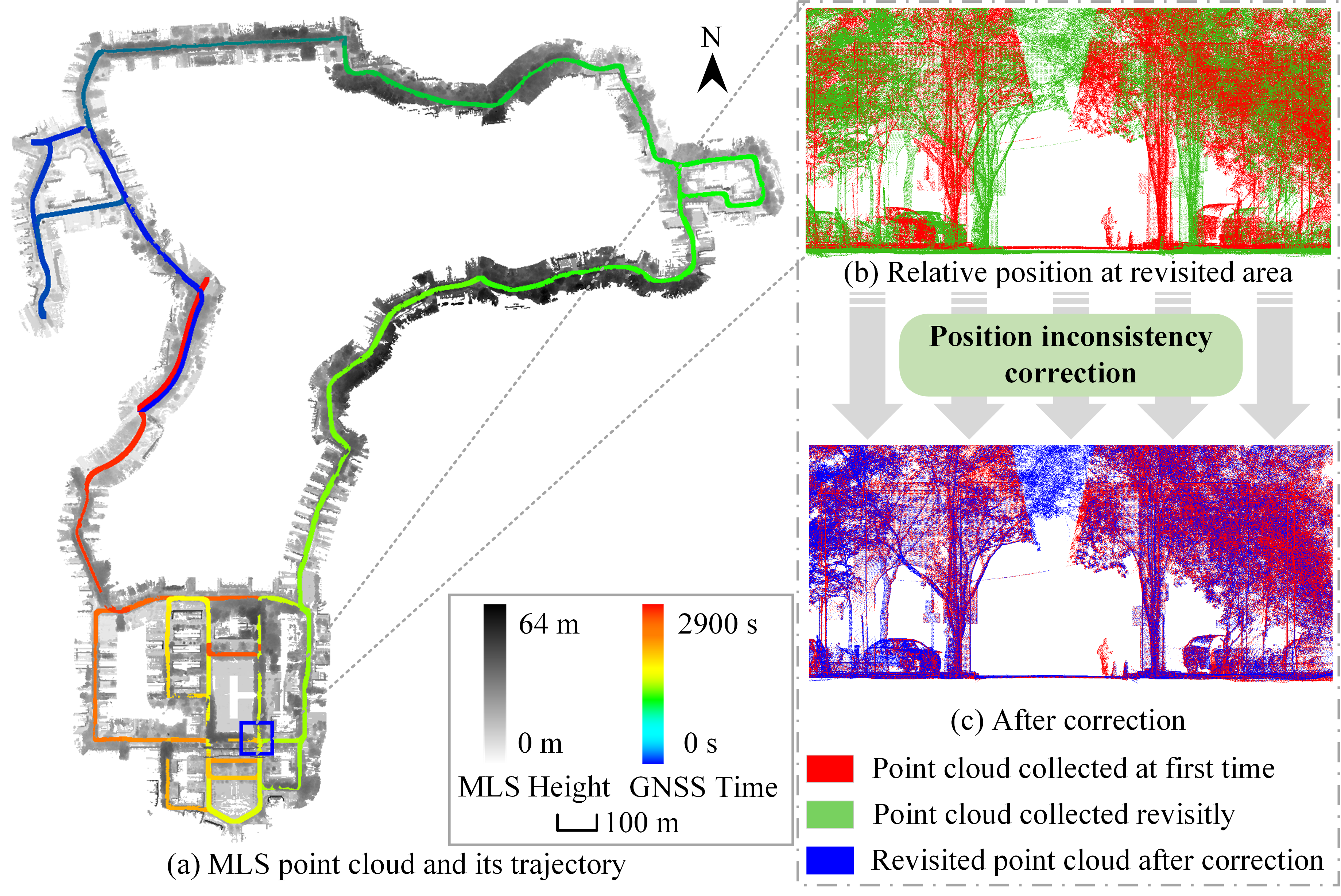
MuCoGraph: A Multi-scale Constraint Enhanced Pose Graph Framework for MLS Point Cloud Inconsistency Correction
Yuhao Li Zou, Xianghong Zou, Tian Li, Sihan Sun, Yuan Wang, Fuxun Liang, Jianping Li†, Bisheng Yang†, Zhen Dong
ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing (IF: 12.7) 2023
We present MuCoGraph, which introduces multi-scale constraints to establish the correct correspondences for revisited areas, and formulates an enhanced pose graph for position inconsistency correction. The proposed method was used to correct the MLS point cloud position inconsistency in three datasets. The average three-dimensional distance of the checkpoints was reduced from 0.362 m, 0.108 m, and 1.027 m to 0.057 m, 0.033 m, and 0.051 m for datasets I, II, and III respectively. In addition, the root-mean-square error of all three datasets was less than 0.04 m after correction. The experiments confirmed that the proposed method can automatically locate and correct the position inconsistency of MLS point clouds, showing good robustness and effectiveness.
